In this cybersecurity tutorial, we will walk you through all the basic concepts required for you to kickstart your journey in cybersecurity.
Today’s modern world is revolving around technology and digital life making us more exposed to cybercrimes than ever before.
Cybercrime causes a potential threat to individuals and organizations leading to huge financial loss. Data breaches are rapidly increasing and the world is turning towards cybersecurity to protect valuable data.
What is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity is a way of protecting the network, computers, and other electronic gadgets from cybercriminals. The Malicious attackers delete, modify or leak confidential information posing a huge threat to a business or an individual.
Cybersecurity helps keep the data out of reach from the attackers by ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability (ICA) of data.
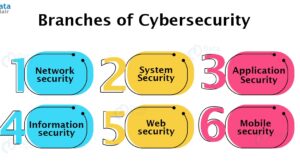
Cybersecurity is made up of the following branches :
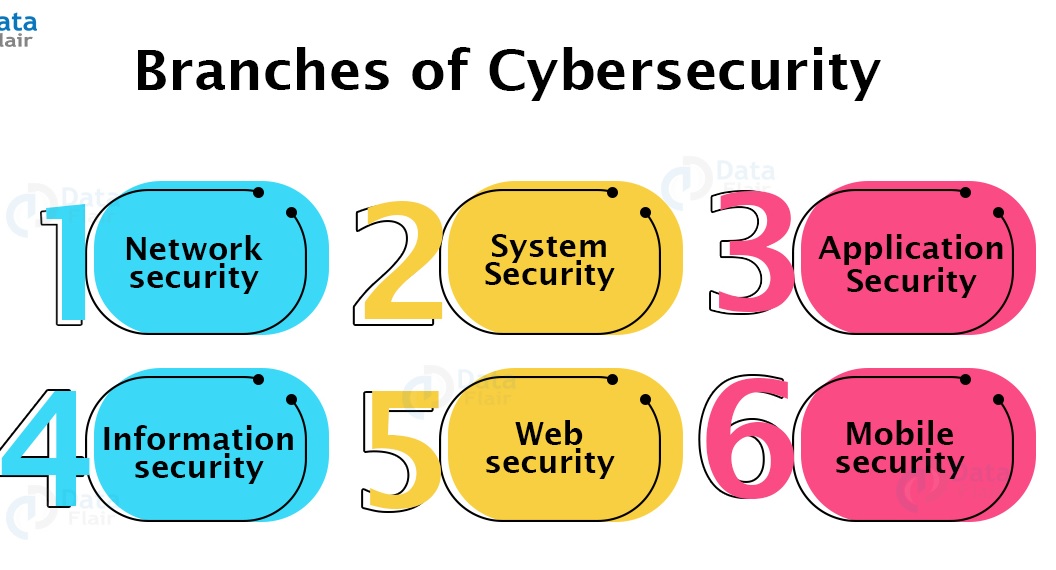
1. Network security
Network security refers to a set of rules and configurations to protect network traffic and data. They prevent data theft by monitoring network connections.
2. System security
Safeguard the system and OS from malicious intrusion, modification, and Virus.
3. Application security
Protects the application from being hijacked.
4. Information security
Secures sensitive information from unauthorized access and prevents misuse, disclosure, or destruction of data.
5. Web security
Protects a web application from security breaches from unauthorized personnel.
6. Mobile security
Protection of all gadgets associated with wireless computing like smartphones tablets and laptops.
History Of Cyber Security
Cybersecurity came into existence as a research project on ARPANET in the year 1972.
Bob Thomas, a researcher, invented the first computer virus and named it “Creeper”. The Creeper moved across the network leaving a trail. Wherever it went, it printed the message “I’M THE CREEPER: CATCH ME IF YOU CAN”.
Ray Tomlinson, the inventor of email created the first antivirus called “Reaper”. Reaper would chase and delete the creeper along its trail. In the late 1990s, when the world entered online, computer viruses turned into serious threats from a mere academic prank.
What is the need for Cyber Security?
The cost of cybersecurity breaches is rising exponentially causing serious financial losses to businesses. The global average cost of a data breach for the year 2019 is $3.92 million, with a 1.5 percent increase from the 2018 survey.
Attackers have increased their complexity of attacks by using smart tactics, throwing a huge challenge for the organization to maintain their security up to the mark.
What can you do with Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity helps us to protect our Network and system resources which contain business crucial information. This is achieved by strengthening the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
The various techniques in cybersecurity help us in protecting the data and minimizing the risk of system breach making the business sustainable.
How does Cyber Security make working so easy?
Cybersecurity makes our day-to-day work very easy by making sure the resources are available in the network as and when required.
A small vulnerability can cause huge damage to the company’s resources and reputation.
Cybersecurity saves the day by reinforcing the privacy, security, and correctness of data.
Damage to business from security breaches
Even the most renowned companies in the world have faced destructive losses from data breaches.
In 2013, Adobe faced a massive breach compromising 3 million customer’s credit card data. The company reported that hackers stole encrypted customer login details. The company had to pay $1.1 million as a legal fee for disclosure of customer records.
Motives behind Cyberattacks
The motive behind cybercrimes can be any of the following:
To damage the reputation of an organization
Financial gain via ransom
Revenge for personal reasons
Political causes
To instill fear
Cyber Criminals and their types
Cyber Criminals are attackers with the motivation to Commit malicious activity to a network. They are of the following types:
1. Script kiddies
These are thrill-seekers and enthusiasts who want to be a hacker but lack technical expertise.
2. Spammers
These criminals spam your inbox with bulk messages. They try to steal your data and perform fraudulent activities.
3. Hacker groups
These are Informal communities that work anonymously with the same motive of breaking the security of a target.
4. Phishers
Phishers try to gain personal details like usernames and passwords. They present themselves as trustworthy entities to obtain this information.
5. Insiders
Disloyal individuals within an organization who are willfully stealing, damaging or exposing internal data of an organization.
6. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Agents
They perfectly execute organized crimes against a target by a long-term presence on a network to mine highly sensitive data.
7. Identity Thieves
They steal the identity of another person without their knowledge to commit fraud like making financial transactions.
Types of Cyber Threats/Attacks
Cyber attacks are of various types:
Based On the attacker’s motivation cyber attacks can be classified into two types.
a. Passive attack
The attacker’s motivation is to gain confidential information without affecting the system resources or threatening the victim.
b. Active attack
The attacker modifies the information and causes a threat to system resources causing damage to the integrity of the system.
The various methods employed by cybercriminals to breach security are as follows
1. Malware
Malware is malicious software made by the hacker to damage a genuine user’s system. It usually spreads when you install rogue software or click an infected link or email.
The different types of malware are:
a. Virus
A virus is a self-replicating computer program that spreads through the computer system infecting other clean files.
b. Trojan horse
It is a corrupted code that looks real and misleads users of its original purpose. If the user is fooled into thinking it’s a harmless file the trojan spreads to other files and harms a computer.
c. Spyware
A code that secretly captures user activities like internet usage data and makes use of the tracked information for fraud purposes.
d. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that locks the user’s system. The attacker demands a ransom to restore access.
e. Botnets
Botnets are devices connected over the internet. It is used for Launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) on the user’s website or to steal data.
2. SQL injection
SQL injection runs a Structured Query Language code in the database of a website to access sensitive data like private customer details.
3. Phishing
Method where cybercriminals steal user data like login credentials and credit card numbers by duping like a trusted party. It is simply launched via email or a text message.
4. Man-in-the-middle attack
MitM attack is of eavesdropping nature, where the unauthorized third party secretly intercepts the communication between two parties.
5. Denial-of-service attack
The attacker cuts down all messages directed to a specific destination. This is done by disrupting a whole network or overloading it with messages to degrade performance.
6. Scareware
The attacker scares the user and tricks him into purchasing an anti-virus. Once it’s installed by the system user, it starts throwing messages on the screen that your system is under fire and throws the victim into a panic. Then it redirects a victim to a bogus website to shop for an anti-virus.
7. Keylogger
Keylogger is a code that downloads the log of all the keystrokes of the system. It is sent to the hacker’s computer, to access sensitive information like user ids and passwords.
Cyber Security Methods
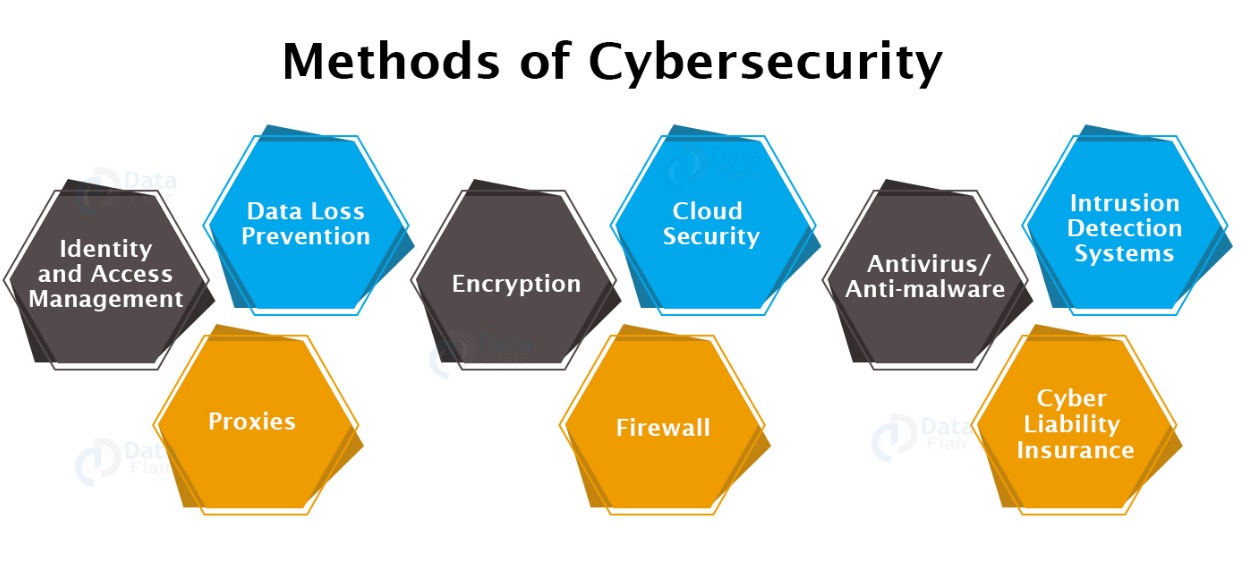
1. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP software spots data breaches by ensuring end users do not send sensitive information outside the corporate network.
2. Cloud Security
Protection of data stored in cloud platforms.
3. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) or Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Monitors the network to identify potentially malicious activity and reports to the management.
4. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Set of policies for managing the access privileges for the individual users in the network.
5. Encryption
Process of encoding raw data into unreadable form to prevent theft in transit.
6. Antivirus/anti-malware
Software that finds and removes viruses and malware from the system.
7. Proxies
It is a hub between the user and the internet. It allows the user to conceal the network id by hiding the user’s IP address.
8. Firewall
Uses a set of predefined rules to set barriers against untrusted networks.
9. Cyber Liability Insurance
Covers financial losses and operational liability from data theft or breaching.
Integrating Automation with Cybersecurity
Automation in cybersecurity allows faster detection of intrusion in the system.
Typically automation in cybersecurity is bringing AI and ML technologies to boost the analytical capability of the company.
Few automation tools are already out in business. Robotic Process Automation(RPA), Security orchestration automation and response (SOAR), security incident, and event management (SIEM) are few examples of automation tools that can benefit the security of a business.
Applications of Cybersecurity
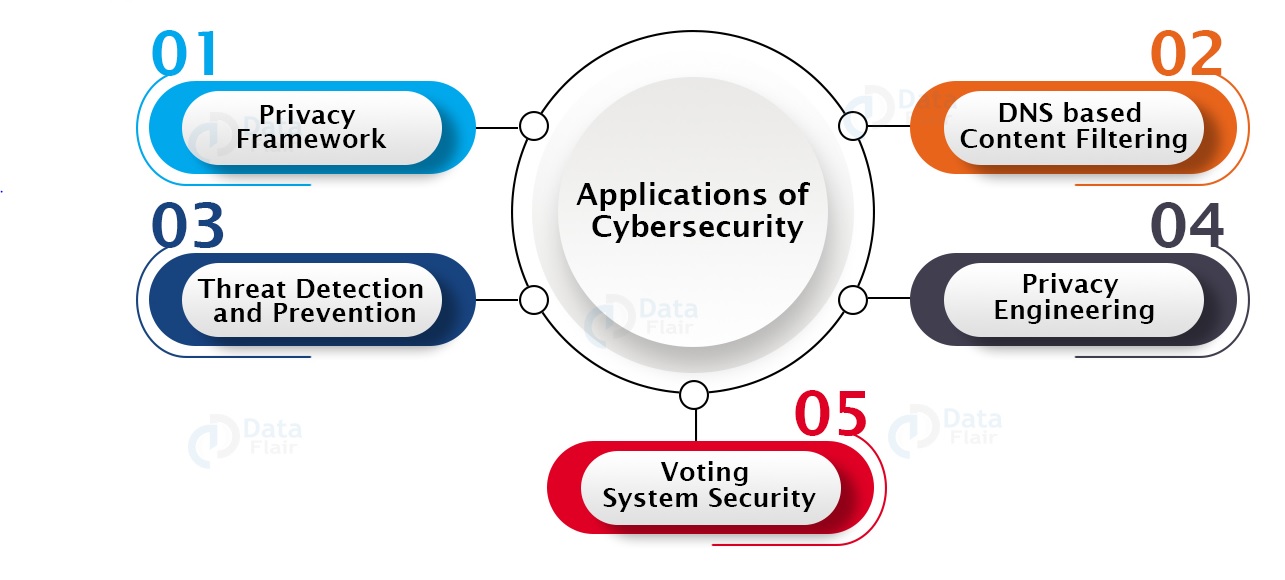
Privacy Framework – It means preventing private data from attackers.
DNS-based content filtering – It means preventing access to websites that harbor malware or ransomware.
Threat detection and prevention – It means identifying the threat and preventing from the same.
Privacy engineering – It means researching the trustworthiness of cyber technology.
Voting system security – It means having a secure voting system during elections.
Advantages of Cybersecurity
The wealth of an organization is its data. Cybersecurity ensures the security and reliability of data.
It restricts unauthorized access protecting the privacy of confidential information.
Safeguards the system from malware and protects the system from being hacked.
Best Practices
Keep your software and Operating system updated.
Install anti-virus software in your system.
Use strong passwords.
Avoid opening emails from unknown sources.
Avoid usage of public Wifi.
Summary
Cybersecurity is the protection of your system against internet fraud. These frauds come in different motivations and use various methods to access your data without your permission.
You can protect your confidential information by using several tools and approaches defined by cybersecurity.